Discover the advantages of choosing a PACS system to digitize the operations of radiology and imaging services.
Digitalization is the transformation of analog processes and physical objects into digital ones. One method to achieve this is to scan physical objects for later storage, either on a hard drive or in the cloud.
In this way, everything that was previously done manually and generated unnecessary costs, thanks to the digitization It has become much more simple, fast, efficient and accessible.
In this regard, the digitization Suppose a great savings in time and resources in the management and storage of radiological studies. In just a few steps you can perform an interpretation and send a report of results, which, using a traditional system, requires much more time.
What do PACS and RIS mean?
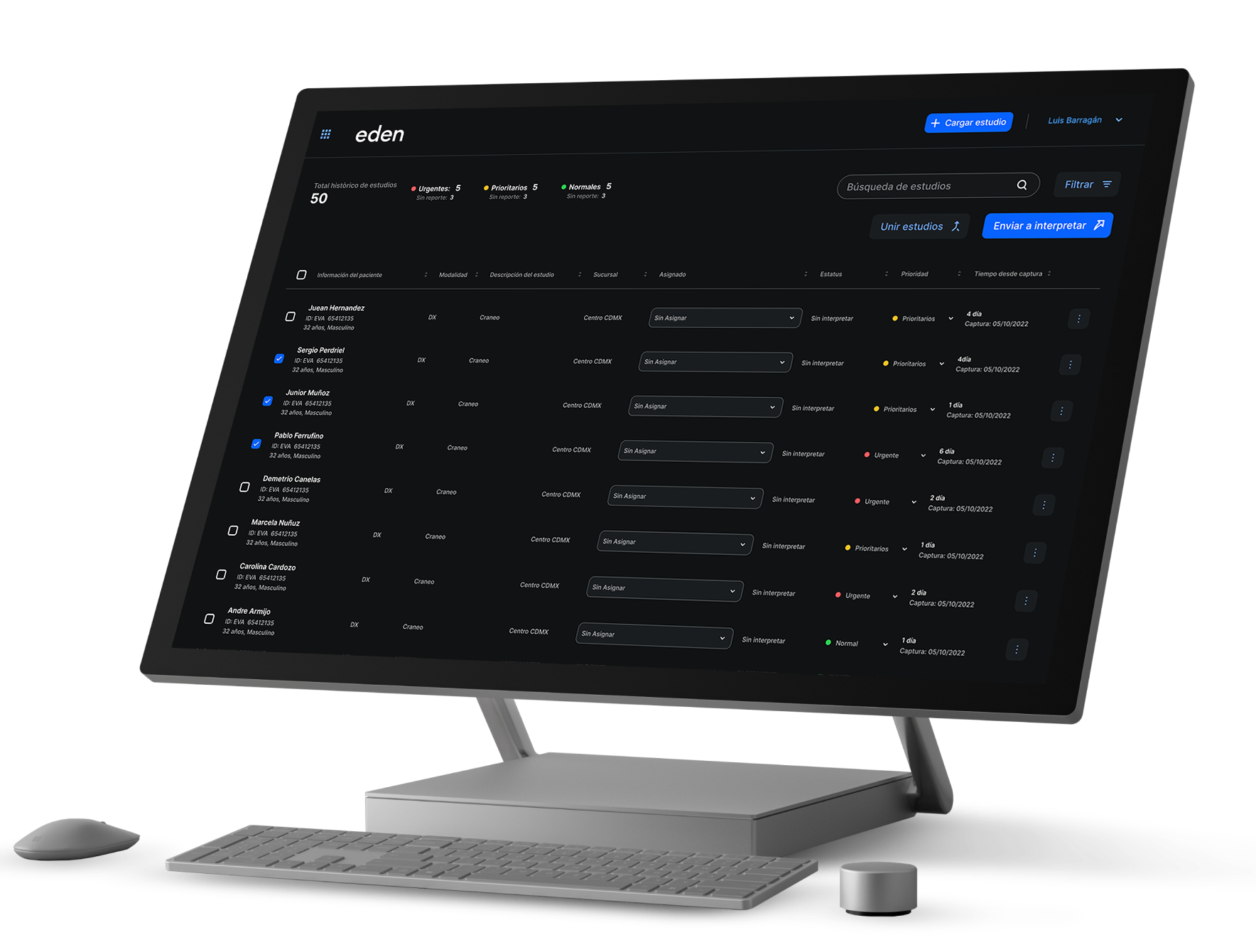
Los PACS They are systems of storage, management and communication of medical images, as indicated by the translation of its initials: Picture Archiving and Communications System. Using this system, clinical images from various diagnostic modalities or methods (X-ray, ultrasound, tomography, magnetic resonance, etc.) can be managed.
On the other hand, RIS is the acronym for Radiology Information System, that is, radiology information system. These systems are responsible for the management of diagnostic imaging departments with various modules.
These modules include: agenda, identification files, registration and codes for patients and examinations, medical reports, billing, statistics, case control, teaching, follow-up cases, instant email and bibliography management, among others.
Both the systems PACS such as RIS have contributed to the digitization process of clinics, hospitals and doctors' offices. As a result, there are significant increases in staff productivity, and a decrease in expenses in different areas.
Medical image processing and digitization
In the mid-80s, a communication standard for digital image was created, which was called DICOM (Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine). It is a protocol that allows the sharing of medical images regardless of the brand of the diagnostic modality.
It can be said that this was the The beginning of digitalization in medicine, since images were obtained that can be transmitted over the network. Subsequently, you can Store on universal devices, thanks to the DICOM format. In the same way, doctors can perform interpretations of studies using a DICOM viewer.
In the beginning, the most used digital images were those from computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging and ultrasound or ultrasound. At present practically all diagnostic modalities are compatible with the DICOM format.
Acquisition of digital medical images
The acquisition of digital images consists of two main modalities: those that are processed directly digitally and those obtained from a Physical board.
In the first case, the information acquired through imaging methods is processed on a computer in binary codes. As a result, the digital image is obtained, which can be stored or communicated through the network.
On the other hand, in the second case, it is digitized manually by means of a X-ray plate digitizer, obtaining numerical information that is processed in the same way to digitize information in an image.
Location of digital medical images
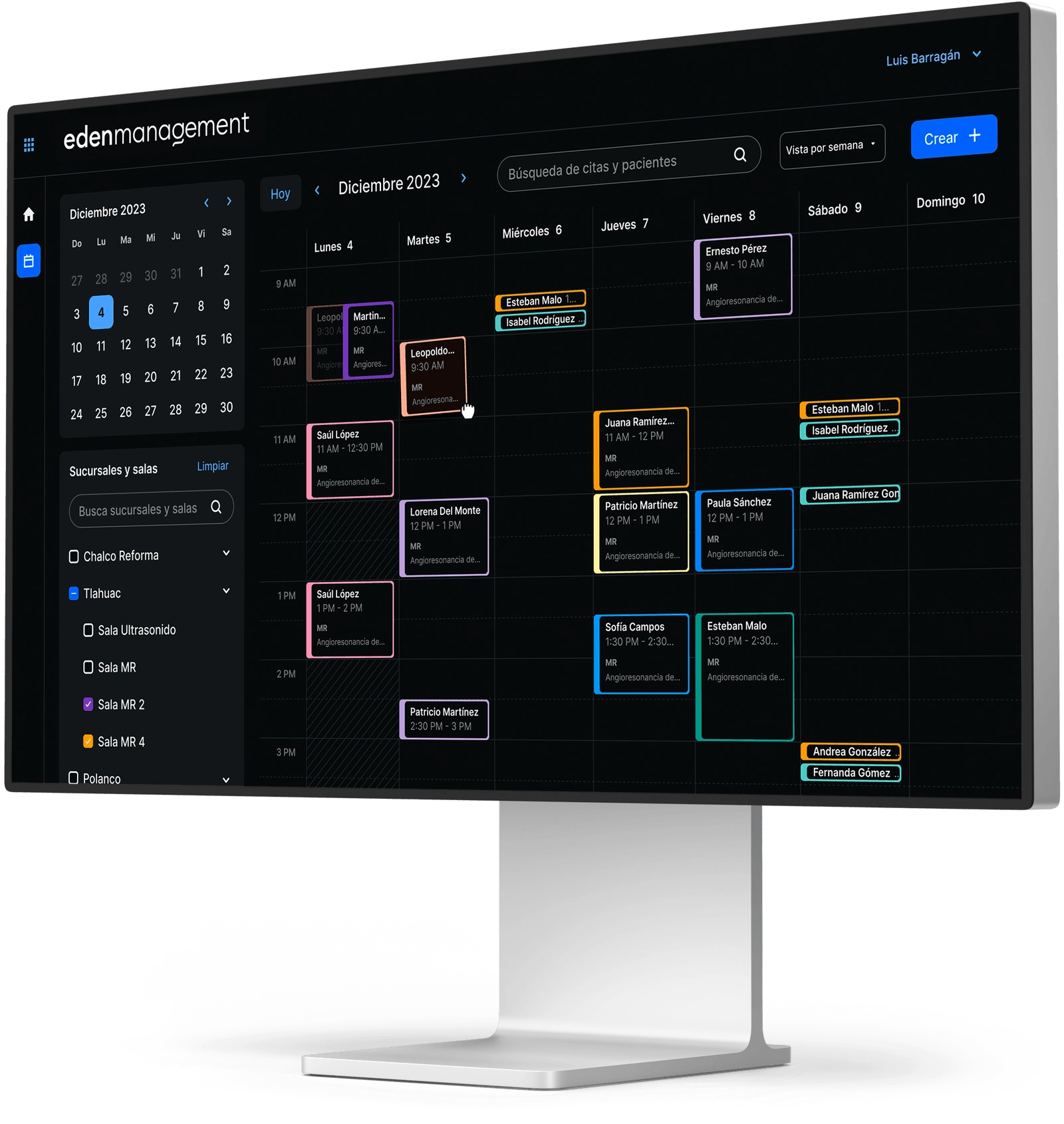
Medical image digitization systems operate in line with the PACS system.
In this way, the storage of the digitized images will reside in two memories: primary and secondary.
Primary Memory (Primary Cache)
This type of memory is made up of server hard drives and is the best known and most used by devices in general.
In this working memory, the PACS system stores the studies it receives or sends and which the PACS Client can access moments later (even in seconds, depending on the systems).
This type of memory has a main Inconvenience: on reduced space. That is why it is a temporary memory that stores few studies at a time. Depending on the available memory, images can be saved from a few weeks to a few months.
Your main Advantage It lies in your high access speed. because the operation of the cache memory in general makes it a quick-access location.
From a technological point of view, the future of PACS systems suggests that computers have an increasing amount of memory of this type, mainly due to the benefit of the cost per Mb that it entails.
Secondary memory (Archive)
This type of memory is being used less and less, especially since the advent of cloud storage services.
Its purpose is to store the studies received by the primary memory of permanent form.
It is characterized by being a location of slow access. It evokes the somewhat manual principles of computer science, since it consists of DLT tapes, MOD optical discs, CDs or DVDs, which are usually stored in a closet or cellar.
Remote memory (PACS Client)
A major benefit of the PACS system is that client stations can be configured with your own storage memory to be able to receive copies of studies without having to request them. This is a great Time savings.
La Disadvantage of this type of memory is its capacity, which is very limited to the type of station.
However, its Great advantage It is the possibility of Dispose immediately from any remote study station.
Benefits of digitizing imaging studies
The purpose of technology is to optimize human tasks, making them more comfortable, faster and accessible to everyone.
This is why the digitization of clinical imaging studies brings with it a series of benefits:
Savings
The reduction of costs in companies, regardless of their area, has been one of the most important effects of digitalization.
In this way, it has been possible to reduce costs in different areas such as production, labor or other resources, thus causing an increase in staff productivity.
In the same way, everything that translates into reduced expenses for the company becomes a more accessible service for users. So, without a doubt, it's a win-win relationship.
Remote access
One of the great benefits of digitizing radiographic plates is the possibility of accessing them remotely, thanks to PACS systems.
Depending on the service provider, as well as the equipment, access to these studies without the need to go to where they were carried out is totally a reality.
In the same way, it enables collaboration between medical specialists without them having to be in the same physical place.
Avoid wear and tear
X-ray plates are susceptible to wear and tear and have a limited lifespan. After a certain time, doctors cannot prepare diagnoses from physical plates.
Instead, a digital image doesn't wear out. This will be useful for making comparisons in the evolution of patients.
It should be mentioned that radiographic plates are very polluting, and discarding them requires special processes that also involve significant expenses.
Other benefits
The digitization of radiology services and PACS systems brings with it others productivity benefits, such as:
- Take advantage of worklists that facilitate the assignment of tasks.
- Verify the workload of the doctors who will interpret the studies.
- Elaboration of medical reports in an expedited manner.
- Do productivity analysis.
In addition, there are tools and utilities such as:
- Recovery of medical records and patient information.
- Recovery of medical reports previous ones.
- All the tools of the DICOM visualizers, which allow more accurate diagnoses.
In this sense, the digitalization of radiological services is aimed at offering better service and care to each patient.
References
- Digital X-ray with phosphor plates (Henry Schein)
- Image storage and transmission. PACS (conganat.org)
- Huang, H. (2018). PACS and Imaging Informatics. Somerset: John Wiley & Sons, Incorporated.















.jpg)


